Category
Popular Articles
- AI (12)
- Android (38)
- App Suggest (4)
- Apple (15)
- Apple TV (2)
- Bluetooth (3)
- Cars (2)
- ChatGpt (1)
- Chrome (2)
- Did you know? (1)
- E-Commerce News (1)
- Ecommerce Websites business (7)
- Electronics Shopping (5)
- Fashion Tips (3)
- Gaming (4)
- Google Gemini (3)
- Hair Care Tips (2)
- How to (13)
- iCloud (1)
- Infotainment System (1)
- Iphone (101)
- Job Posting (1)
- Lifestyle (3)
- Mac (20)
- Mobile Games (1)
- Netflix (1)
- Online Shopping Websites (2)
- Personal Finance Management (3)
- Product Reviews (3)
- Roku TV (4)
- Samsung (9)
- Shopping Tips (10)
- Spotify (1)
- Tech (92)
- Windows 11 (18)
- Zero Waste (3)
Discounted Products
-
 Leo Creation 144 TC Cotton Double Jaipuri Prints Flat Bedsheet(Pack of 1, Blue, Gree, Red, Grey, Light Grey)
Leo Creation 144 TC Cotton Double Jaipuri Prints Flat Bedsheet(Pack of 1, Blue, Gree, Red, Grey, Light Grey)
₹2,999.00Original price was: ₹2,999.00.₹329.00Current price is: ₹329.00. -
 Home Garage 210 TC Cotton King Floral Fitted (Elastic) Bedsheet(Pack of 1, Grey)
Home Garage 210 TC Cotton King Floral Fitted (Elastic) Bedsheet(Pack of 1, Grey)
₹999.00Original price was: ₹999.00.₹299.00Current price is: ₹299.00. -
 Goodrik 140 TC Cotton Double 3D Printed Flat Bedsheet(Pack of 1, Brown)
Goodrik 140 TC Cotton Double 3D Printed Flat Bedsheet(Pack of 1, Brown)
₹499.00Original price was: ₹499.00.₹229.00Current price is: ₹229.00. -
 GLOBALSHOP 350 TC Microfiber Double Floral Flat Bedsheet(Pack of 1, Multicolor)
GLOBALSHOP 350 TC Microfiber Double Floral Flat Bedsheet(Pack of 1, Multicolor)
₹1,250.00Original price was: ₹1,250.00.₹263.00Current price is: ₹263.00. -
 RisingStar 250 TC Microfiber King Printed Fitted (Elastic) Bedsheet(Pack of 1, FITTED-ROUND-CIRCLES-PREMIUM)
RisingStar 250 TC Microfiber King Printed Fitted (Elastic) Bedsheet(Pack of 1, FITTED-ROUND-CIRCLES-PREMIUM)
₹2,299.00Original price was: ₹2,299.00.₹299.00Current price is: ₹299.00. -
 Home Garage 210 TC Cotton King Floral Fitted (Elastic) Bedsheet(Pack of 1, Fitted Black Green)
Home Garage 210 TC Cotton King Floral Fitted (Elastic) Bedsheet(Pack of 1, Fitted Black Green)
₹1,299.00Original price was: ₹1,299.00.₹299.00Current price is: ₹299.00. -
 Home Garage 180 TC Cotton King 3D Printed Flat Bedsheet(Pack of 1, White)
Home Garage 180 TC Cotton King 3D Printed Flat Bedsheet(Pack of 1, White)
₹999.00Original price was: ₹999.00.₹229.00Current price is: ₹229.00. -
 Home Sizzler 153 cm (5 ft) Polyester Room Darkening Window Curtain (Pack Of 2)(Floral, Maroon)
Home Sizzler 153 cm (5 ft) Polyester Room Darkening Window Curtain (Pack Of 2)(Floral, Maroon)
₹799.00Original price was: ₹799.00.₹299.00Current price is: ₹299.00. -
 Panipat Textile Hub 152.4 cm (5 ft) Polyester Window Curtain (Pack Of 2)(Solid, Aqua)
Panipat Textile Hub 152.4 cm (5 ft) Polyester Window Curtain (Pack Of 2)(Solid, Aqua)
₹1,899.00Original price was: ₹1,899.00.₹299.00Current price is: ₹299.00. -
 Home Sizzler 214 cm (7 ft) Polyester Semi Transparent Door Curtain (Pack Of 2)(Floral, Maroon)
Home Sizzler 214 cm (7 ft) Polyester Semi Transparent Door Curtain (Pack Of 2)(Floral, Maroon)
₹1,199.00Original price was: ₹1,199.00.₹399.00Current price is: ₹399.00. -
 Home Sizzler 153 cm (5 ft) Polyester Room Darkening Window Curtain (Pack Of 2)(Floral, Brown)
Home Sizzler 153 cm (5 ft) Polyester Room Darkening Window Curtain (Pack Of 2)(Floral, Brown)
₹799.00Original price was: ₹799.00.₹299.00Current price is: ₹299.00. -
 Stella Creations 214 cm (7 ft) Polyester Room Darkening Door Curtain (Pack Of 2)(Abstract, Brown)
Stella Creations 214 cm (7 ft) Polyester Room Darkening Door Curtain (Pack Of 2)(Abstract, Brown)
₹1,299.00Original price was: ₹1,299.00.₹449.00Current price is: ₹449.00. -
 Homefab India 152.5 cm (5 ft) Polyester Room Darkening Window Curtain (Pack Of 2)(Floral, Light Blue)
Homefab India 152.5 cm (5 ft) Polyester Room Darkening Window Curtain (Pack Of 2)(Floral, Light Blue)
₹1,199.00Original price was: ₹1,199.00.₹319.00Current price is: ₹319.00. -
 Urban Home 214 cm (7 ft) PVC Transparent Door Curtain Single Curtain(Solid, Off White)
Urban Home 214 cm (7 ft) PVC Transparent Door Curtain Single Curtain(Solid, Off White)
₹699.00Original price was: ₹699.00.₹203.00Current price is: ₹203.00. -
 Panipat Textile Hub 213 cm (7 ft) Polyester Door Curtain (Pack Of 2)(Solid, Brown)
Panipat Textile Hub 213 cm (7 ft) Polyester Door Curtain (Pack Of 2)(Solid, Brown)
₹1,199.00Original price was: ₹1,199.00.₹349.00Current price is: ₹349.00.
Affiliate Links
Promotion
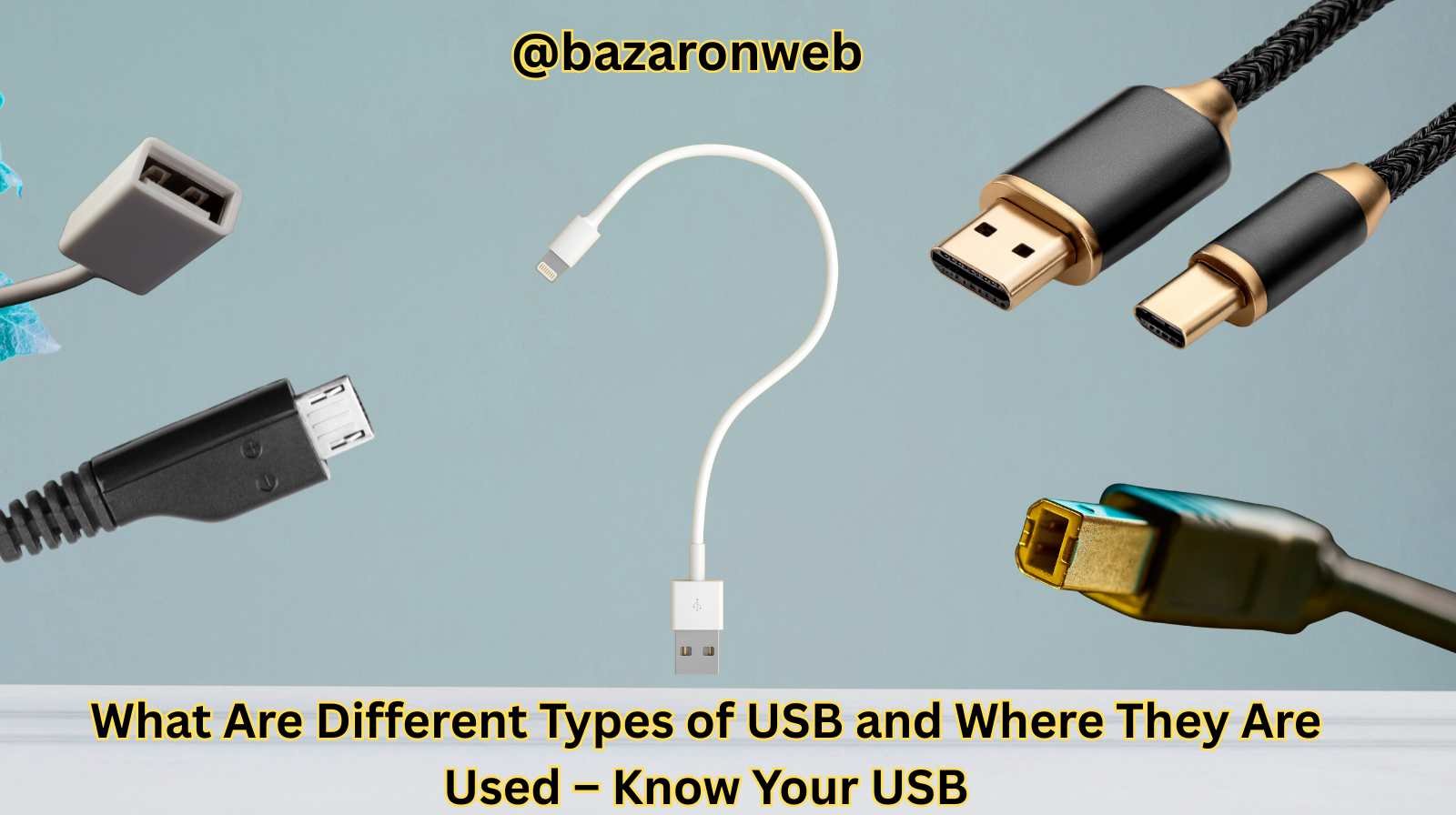
Introduction
Universal Serial Bus, or USB, is something we all use daily — whether it’s charging our smartphones, transferring data, or connecting devices like printers, keyboards, and external drives. It’s one of the most essential yet overlooked technologies that power our digital lives.
But did you know there are different types of USB connectors and versions, each designed for specific purposes? From the chunky USB-A ports you find on laptops to the sleek and reversible USB-C ports on modern devices, understanding these differences can save you frustration, money, and time.
In this article, I’ll walk you through the various types of USB, their features, and where you’ll most likely encounter them.
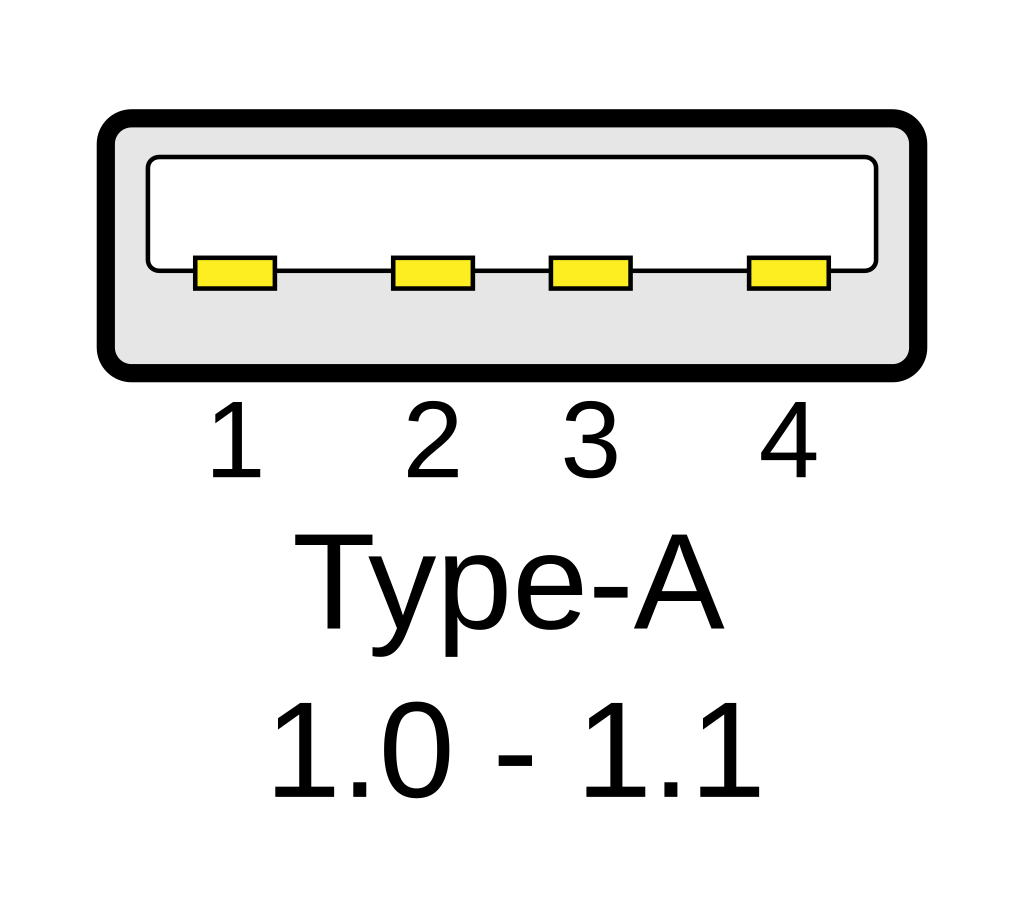
1. USB-A (Standard-A)
What It Is
The USB-A connector is the most recognizable and widely used USB type. It’s rectangular, flat, and has been around since the late 1990s.
Where You’ll See It
- Laptops and desktop computers (especially older models)
- Flash drives (USB sticks)
- Keyboards and mice
- Printers and external hard drives
Image Credit: By Nicola02nb – Own work, CC BY-SA 4.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=117668209
Why It Matters
USB-A has been the foundation of connectivity for decades. However, it’s not reversible, which means you need to plug it in the correct way. In terms of speed, it depends on the USB version (2.0, 3.0, or 3.1).
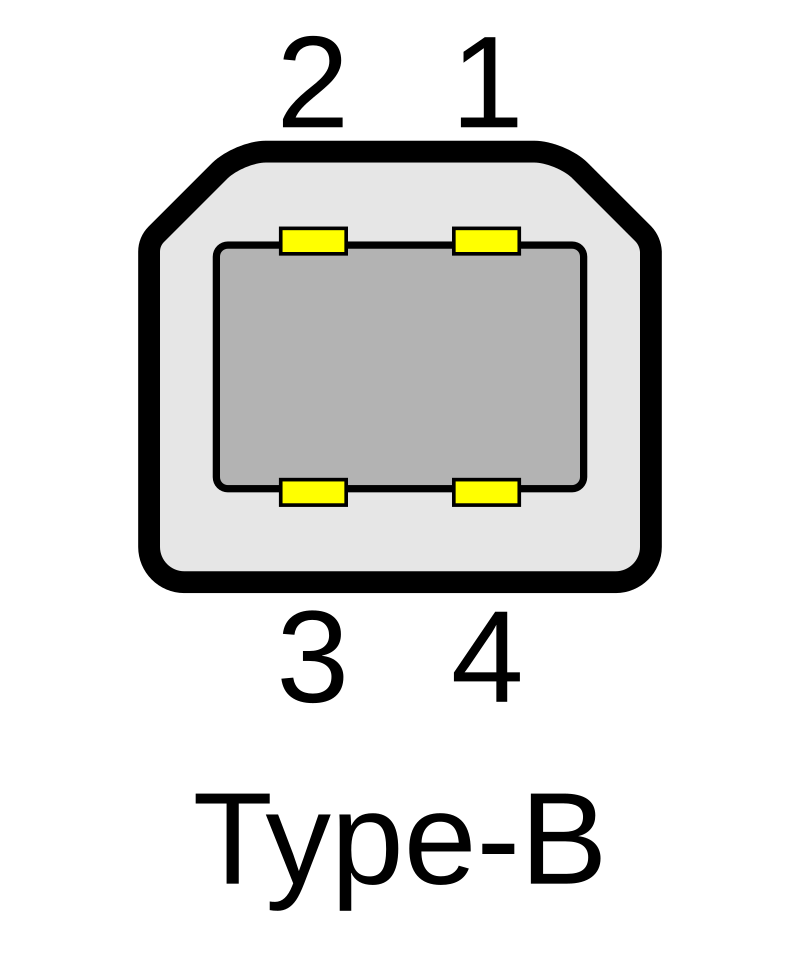
2. USB-B (Standard-B)
What It Is
USB-B is a square-shaped connector with a slight bevel at the top. You won’t find it on small gadgets, but it’s still used for heavier-duty devices.
Where You’ll See It
- Printers
- Scanners
- Some external hard drives
- Audio interfaces
Image Credit: By Fred the Oyster, CC BY-SA 4.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=36171387
Why It Matters
USB-B is less common today but remains important for larger peripherals that require stable connections.
3. Mini-USB
What It Is
As the name suggests, Mini-USB is smaller than standard USB-A or USB-B. It was popular in the early 2000s before Micro-USB took over.
Where You’ll See It
- Older cameras
- MP3 players
- Early-generation smartphones and GPS units
Why It Matters
Mini-USB is mostly obsolete now, but you might still have some old gadgets or drives that need it.
4. Micro-USB
What It Is
Micro-USB became the industry standard for smartphones, tablets, and accessories for many years. It’s smaller and thinner than Mini-USB.
Where You’ll See It
- Android smartphones (pre-USB-C era)
- Power banks
- Bluetooth headphones and speakers
- Some cameras and controllers
Why It Matters
Micro-USB is being phased out in favor of USB-C, but it’s still widely found in budget devices and accessories. It only fits one way, which can sometimes be annoying.
5. USB-C
What It Is
USB-C is the modern, sleek, and reversible connector that’s now becoming the universal standard. It supports faster data transfer and higher power delivery compared to older types.
Where You’ll See It
- Latest iPhones and Android smartphones
- MacBooks and modern laptops
- Tablets
- Portable gaming consoles like the Nintendo Switch
- External SSDs and docking stations
Image credit By Chindi.ap, CC BY-SA 4.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=52579223
Why It Matters
USB-C is versatile. It supports charging, data transfer, and video output through one port. It’s also the standard for USB4 and Thunderbolt 4, making it future-proof.
6. Lightning (Apple’s Proprietary USB)
What It Is
While not a standard USB, Apple’s Lightning connector deserves a mention. It was introduced in 2012 and used on iPhones, iPads, and some accessories.
Where You’ll See It
- iPhones up to iPhone 14
- iPads (non-Pro versions until recently)
- AirPods charging cases
- Apple accessories like Magic Mouse and Magic Keyboard
Why It Matters
Lightning was Apple’s solution before USB-C. However, with EU regulations and global standardization, Apple is transitioning fully to USB-C starting with iPhone 15 and beyond.
7. USB Versions Explained
Aside from physical types, USB also has different versions that determine speed and performance.
- USB 2.0 – Introduced in 2000, with speeds up to 480 Mbps. Common for keyboards, mice, and flash drives.
- USB 3.0 / 3.1 / 3.2 – Much faster (5–20 Gbps). Recognizable by blue-colored ports. Used in external SSDs, gaming accessories, and high-speed drives.
- USB4 – Latest generation with speeds up to 40 Gbps. Built on USB-C. Supports multiple protocols including video, data, and charging.
8. Specialized USB Types
USB OTG (On-The-Go)
- Lets smartphones act as hosts for USB devices like keyboards or storage.
- Useful for transferring data without a computer.
USB Thunderbolt (via USB-C)
- Found on high-end laptops and Macs.
- Combines USB, DisplayPort, and power delivery in one port.
Magnetic USB Connectors
- Found in accessories or third-party cables.
- Provide easier plug-in for charging.
Where Each USB Type Is Commonly Used
Here’s a quick summary:
| USB Type | Common Devices |
|---|---|
| USB-A | PCs, flash drives, mice, keyboards |
| USB-B | Printers, scanners |
| Mini-USB | Older cameras, MP3 players |
| Micro-USB | Power banks, headphones, budget phones |
| USB-C | Modern smartphones, laptops, SSDs, gaming consoles |
| Lightning | Apple iPhones, iPads, AirPods |
| USB 3.0+ | External drives, gaming accessories |
| USB4 | High-end laptops, docking stations |
Future of USB
The future is clearly USB-C and USB4. Governments and manufacturers are pushing for a single, universal standard to reduce electronic waste and improve user experience. This means fewer cables to carry, faster speeds, and higher compatibility across devices.
Apple, once resistant, has now embraced USB-C, which will likely cement it as the dominant connector of the next decade.
Conclusion
USB technology has come a long way since its introduction in the late 90s. From USB-A’s reliability to USB-C’s versatility, each type has played an important role in connecting our devices. While older types like Mini-USB and Micro-USB are fading away, USB-C is clearly leading the charge as the one port to rule them all.
So the next time you’re shopping for a gadget or cable, remember this guide — because knowing your USB type ensures you always get the right speed, compatibility, and performance.
Written by Bazaronweb
Latest Tech Articles
- 5 Ways to Backup and Restore Registry Settings in Windows

- iMessage Not Syncing Between iPhone & Mac? 8 Proven Ways to Fix Account & Device Issues

- Outlook Not Receiving Emails? 8 Proven Fixes for Windows, Mac & Mobile

- Zoom Not Connecting? 7 Ways to Fix Meeting Join Errors on Windows & Mac

- Microsoft Teams Not Opening? 5 Proven Fixes to Restart Your Workspace

Products
-
![Apple Watch Ultra 3 [GPS + Cellular 49mm] Running & Multisport Smartwatch w/Rugged Titanium Case w/Black Titanium Milanese Loop - M. Satellite Communications, Advanced Health & Fitness Tracking](https://bazaronweb.com/retailstores/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/apple-watch-320x320.jpg) Apple Watch Ultra 3 [GPS + Cellular 49mm] Running & Multisport Smartwatch w/Rugged Titanium Case w/Black Titanium Milanese Loop - M. Satellite Communications, Advanced Health & Fitness Tracking
Apple Watch Ultra 3 [GPS + Cellular 49mm] Running & Multisport Smartwatch w/Rugged Titanium Case w/Black Titanium Milanese Loop - M. Satellite Communications, Advanced Health & Fitness Tracking
-
 Apple iPad mini (A17 Pro): Apple Intelligence, 8.3-inch Liquid Retina Display, 256GB, Wi-Fi 6E, 12MP Front/12MP Back Camera, Touch ID, All-Day Battery Life — Purple
Apple iPad mini (A17 Pro): Apple Intelligence, 8.3-inch Liquid Retina Display, 256GB, Wi-Fi 6E, 12MP Front/12MP Back Camera, Touch ID, All-Day Battery Life — Purple
-
 Apple AirPods Max Wireless Over-Ear Headphones, Active Noise Cancelling, Transparency Mode, Personalized Spatial Audio, Dolby Atmos, Bluetooth Headphones for iPhone – Space Gray
Apple AirPods Max Wireless Over-Ear Headphones, Active Noise Cancelling, Transparency Mode, Personalized Spatial Audio, Dolby Atmos, Bluetooth Headphones for iPhone – Space Gray
-
 Apple AirPods Pro 2 Wireless Earbuds, Active Noise Cancellation, Hearing Aid Feature, Bluetooth Headphones, Transparency, Personalized Spatial Audio, High-Fidelity Sound, H2 Chip, USB-C Charging
Apple AirPods Pro 2 Wireless Earbuds, Active Noise Cancellation, Hearing Aid Feature, Bluetooth Headphones, Transparency, Personalized Spatial Audio, High-Fidelity Sound, H2 Chip, USB-C Charging
-
 Leo Creation 144 TC Cotton Double Jaipuri Prints Flat Bedsheet(Pack of 1, Blue, Gree, Red, Grey, Light Grey)
Leo Creation 144 TC Cotton Double Jaipuri Prints Flat Bedsheet(Pack of 1, Blue, Gree, Red, Grey, Light Grey)
₹2,999.00Original price was: ₹2,999.00.₹329.00Current price is: ₹329.00.
Leave a Reply