Category
Popular Articles
- AI (17)
- Android (48)
- App Suggest (13)
- Apple (42)
- Apple TV (4)
- Bluetooth (3)
- Cars (2)
- ChatGpt (1)
- Chrome (2)
- Did you know? (1)
- E-Commerce News (1)
- Ecommerce Websites business (7)
- Electronics Shopping (5)
- Fashion Tips (3)
- Gaming (5)
- Google Gemini (3)
- Hair Care Tips (2)
- How to (13)
- iCloud (1)
- Infotainment System (1)
- Iphone (145)
- Job Posting (1)
- Lifestyle (3)
- Mac (25)
- Mobile Games (1)
- Netflix (1)
- Online Shopping Websites (2)
- Personal Finance Management (3)
- Product Reviews (3)
- Roku TV (4)
- Samsung (10)
- Shopping Tips (13)
- Spotify (1)
- Tech (153)
- VPN (2)
- Windows 11 (38)
- Zero Waste (3)
Discounted Products
-
 Leo Creation 144 TC Cotton Double Jaipuri Prints Flat Bedsheet(Pack of 1, Blue, Gree, Red, Grey, Light Grey)
Leo Creation 144 TC Cotton Double Jaipuri Prints Flat Bedsheet(Pack of 1, Blue, Gree, Red, Grey, Light Grey)
₹2,999.00Original price was: ₹2,999.00.₹329.00Current price is: ₹329.00. -
 Home Garage 210 TC Cotton King Floral Fitted (Elastic) Bedsheet(Pack of 1, Grey)
Home Garage 210 TC Cotton King Floral Fitted (Elastic) Bedsheet(Pack of 1, Grey)
₹999.00Original price was: ₹999.00.₹299.00Current price is: ₹299.00. -
 Goodrik 140 TC Cotton Double 3D Printed Flat Bedsheet(Pack of 1, Brown)
Goodrik 140 TC Cotton Double 3D Printed Flat Bedsheet(Pack of 1, Brown)
₹499.00Original price was: ₹499.00.₹229.00Current price is: ₹229.00. -
 GLOBALSHOP 350 TC Microfiber Double Floral Flat Bedsheet(Pack of 1, Multicolor)
GLOBALSHOP 350 TC Microfiber Double Floral Flat Bedsheet(Pack of 1, Multicolor)
₹1,250.00Original price was: ₹1,250.00.₹263.00Current price is: ₹263.00. -
 RisingStar 250 TC Microfiber King Printed Fitted (Elastic) Bedsheet(Pack of 1, FITTED-ROUND-CIRCLES-PREMIUM)
RisingStar 250 TC Microfiber King Printed Fitted (Elastic) Bedsheet(Pack of 1, FITTED-ROUND-CIRCLES-PREMIUM)
₹2,299.00Original price was: ₹2,299.00.₹299.00Current price is: ₹299.00. -
 Home Garage 210 TC Cotton King Floral Fitted (Elastic) Bedsheet(Pack of 1, Fitted Black Green)
Home Garage 210 TC Cotton King Floral Fitted (Elastic) Bedsheet(Pack of 1, Fitted Black Green)
₹1,299.00Original price was: ₹1,299.00.₹299.00Current price is: ₹299.00. -
 Home Garage 180 TC Cotton King 3D Printed Flat Bedsheet(Pack of 1, White)
Home Garage 180 TC Cotton King 3D Printed Flat Bedsheet(Pack of 1, White)
₹999.00Original price was: ₹999.00.₹229.00Current price is: ₹229.00. -
 Home Sizzler 153 cm (5 ft) Polyester Room Darkening Window Curtain (Pack Of 2)(Floral, Maroon)
Home Sizzler 153 cm (5 ft) Polyester Room Darkening Window Curtain (Pack Of 2)(Floral, Maroon)
₹799.00Original price was: ₹799.00.₹299.00Current price is: ₹299.00. -
 Panipat Textile Hub 152.4 cm (5 ft) Polyester Window Curtain (Pack Of 2)(Solid, Aqua)
Panipat Textile Hub 152.4 cm (5 ft) Polyester Window Curtain (Pack Of 2)(Solid, Aqua)
₹1,899.00Original price was: ₹1,899.00.₹299.00Current price is: ₹299.00. -
 Home Sizzler 214 cm (7 ft) Polyester Semi Transparent Door Curtain (Pack Of 2)(Floral, Maroon)
Home Sizzler 214 cm (7 ft) Polyester Semi Transparent Door Curtain (Pack Of 2)(Floral, Maroon)
₹1,199.00Original price was: ₹1,199.00.₹399.00Current price is: ₹399.00. -
 Home Sizzler 153 cm (5 ft) Polyester Room Darkening Window Curtain (Pack Of 2)(Floral, Brown)
Home Sizzler 153 cm (5 ft) Polyester Room Darkening Window Curtain (Pack Of 2)(Floral, Brown)
₹799.00Original price was: ₹799.00.₹299.00Current price is: ₹299.00. -
 Stella Creations 214 cm (7 ft) Polyester Room Darkening Door Curtain (Pack Of 2)(Abstract, Brown)
Stella Creations 214 cm (7 ft) Polyester Room Darkening Door Curtain (Pack Of 2)(Abstract, Brown)
₹1,299.00Original price was: ₹1,299.00.₹449.00Current price is: ₹449.00. -
 Homefab India 152.5 cm (5 ft) Polyester Room Darkening Window Curtain (Pack Of 2)(Floral, Light Blue)
Homefab India 152.5 cm (5 ft) Polyester Room Darkening Window Curtain (Pack Of 2)(Floral, Light Blue)
₹1,199.00Original price was: ₹1,199.00.₹319.00Current price is: ₹319.00. -
 Urban Home 214 cm (7 ft) PVC Transparent Door Curtain Single Curtain(Solid, Off White)
Urban Home 214 cm (7 ft) PVC Transparent Door Curtain Single Curtain(Solid, Off White)
₹699.00Original price was: ₹699.00.₹203.00Current price is: ₹203.00. -
 Panipat Textile Hub 213 cm (7 ft) Polyester Door Curtain (Pack Of 2)(Solid, Brown)
Panipat Textile Hub 213 cm (7 ft) Polyester Door Curtain (Pack Of 2)(Solid, Brown)
₹1,199.00Original price was: ₹1,199.00.₹349.00Current price is: ₹349.00.
Affiliate Links
Promotion
Introduction
As someone who works in tech and juggles multiple tools every day, I’m always looking for smarter ways to test, learn, and experiment without putting my main system at risk. Whether it’s trying a new operating system, testing software compatibility, or exploring Linux for a side project, I don’t want to break my primary Windows setup in the process. That’s exactly where VirtualBox comes in.
If you’ve ever wished you could run another operating system inside your Windows 11 PC — without buying a second laptop or reinstalling Windows — VirtualBox makes that possible. It lets you create a virtual computer inside your real one. And the best part? It’s free, powerful, and widely used by developers, students, IT professionals, and curious learners alike.
I often recommend VirtualBox to people who want to learn new tech skills safely. You can experiment, make mistakes, break things, and simply delete the virtual machine if something goes wrong — no damage to your actual PC. For busy professionals, parents, or students, that kind of flexibility is priceless.
In this guide, I’ll explain what VirtualBox is, how it works, and why it’s such a useful tool on Windows 11. If you’re new to virtualization, don’t worry — I’ll keep things clear, practical, and beginner-friendly.
What is VirtualBox?
VirtualBox is a virtualization software that allows you to run one or more operating systems on your computer at the same time — inside a virtual environment. Think of it as creating a “computer within your computer.” Your Windows 11 PC remains your main system (called the host), while VirtualBox lets you install other operating systems (called guests) such as Linux, another version of Windows, or even older operating systems.
VirtualBox is developed and maintained by Oracle, and it’s available for Windows, macOS, and Linux. On Windows 11, it works as an application that uses your PC’s hardware — CPU, RAM, storage, and network — but keeps everything safely isolated from your main system.
This isolation is what makes VirtualBox so powerful. Anything you do inside a virtual machine stays inside it. If a program crashes, a virus infects the virtual OS, or settings get messed up, your real Windows 11 installation is untouched. You can simply shut down or delete the virtual machine and start fresh.
How VirtualBox Works (In Simple Terms)
VirtualBox uses your computer’s hardware virtualization features (like Intel VT-x or AMD-V) to simulate a complete computer system. Inside that simulation, you install an operating system just like you would on a real PC.
Each virtual machine has:
-
its own virtual hard drive
-
allocated RAM and CPU cores
-
virtual graphics and network adapters
-
its own operating system and apps
To Windows 11, VirtualBox is just another program. But to the guest OS, it feels like a real computer.
Why People Use VirtualBox
From my experience, people use VirtualBox for many practical reasons:
-
Learning and education – Students use it to practice Linux, networking, cybersecurity, or server administration
-
Software testing – Developers test apps across different operating systems
-
Safe experimentation – Try unknown software without risking your main system
-
Running legacy software – Use older operating systems for compatibility
-
Work separation – Keep work tools isolated from personal files
I’ve personally used VirtualBox to test beta software, explore Linux distributions, and run clean environments for training sessions — all without worrying about breaking my Windows setup.
Is VirtualBox Safe to Use?
Yes, VirtualBox is considered safe when downloaded from its official source. Since virtual machines are sandboxed, they actually add a layer of protection when experimenting with new tools or systems. Of course, like any software, it should be kept updated and used responsibly.
Why VirtualBox is Great for Windows 11 Users
Windows 11 has strong hardware requirements and modern security features. VirtualBox complements that by letting you:
-
test older Windows versions
-
run Linux alongside Windows
-
explore IT skills without dual-booting
-
avoid complex system changes
For anyone curious about technology — especially those balancing work, family, and learning — VirtualBox offers freedom without risk.
In the next sections, we’ll look at how to download and install VirtualBox on a Windows 11 PC, step by step, so you can start using it confidently.
How to Download and Install VirtualBox on a Windows 11 PC
If you’ve decided to try VirtualBox, you’re already on the right track. I always tell people that installing VirtualBox is one of those “looks intimidating, but is actually simple” tasks. Once you know where to download it from and what to click during installation, the whole process takes less than 10 minutes — even if you’ve never worked with virtualization before.
Below, I’ll walk you through the entire process step by step, exactly as I’d explain it to a colleague or a student.
Step 1: Check System Requirements Before Installing
Before downloading anything, it’s important to make sure your Windows 11 PC is ready for VirtualBox.
Your system should meet these basic requirements:
-
Windows 11 (64-bit)
-
At least 8 GB RAM recommended (4 GB minimum, but 8 GB is more comfortable)
-
At least 20–30 GB free disk space
-
A processor that supports hardware virtualization (Intel VT-x or AMD-V)
-
Virtualization enabled in BIOS/UEFI
Most modern laptops running Windows 11 already meet these requirements. If your PC supports Windows 11, it almost certainly supports virtualization — it may just need to be enabled.
To check virtualization status:
-
Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc → open Task Manager
-
Go to the Performance tab → click CPU
-
Look for Virtualization: Enabled
If it says Disabled, you’ll need to enable it in BIOS before proceeding (something many users only need to do once).
Step 2: Download VirtualBox from the Official Website
To stay safe, always download VirtualBox from the official source.
VirtualBox is developed and maintained by Oracle, and the official download page is the only place you should trust.
Here’s how to do it:
-
Open any browser on your Windows 11 PC (Edge, Chrome, Firefox).
-
Search for “VirtualBox download”.
-
Open the official VirtualBox website.
-
On the download page, you’ll see different platform options.
-
Click Windows hosts.
This downloads a file named something like:
VirtualBox-x.x.x-Win.exe
The file size is usually around 100–120 MB, so the download should finish quickly on most connections.
Step 3: (Optional but Recommended) Download the Extension Pack
Right below the main download link, you’ll see VirtualBox Extension Pack.
I always recommend downloading this at the same time because it adds useful features such as:
-
USB 2.0 and USB 3.0 device support
-
Improved mouse and keyboard handling
-
Better display integration
-
Remote desktop support (RDP)
-
Disk encryption support
Make sure the Extension Pack version matches the VirtualBox version you downloaded.
You don’t install it yet — just download it and keep it ready.
Step 4: Run the VirtualBox Installer
Once the download is complete:
-
Open your Downloads folder.
-
Double-click the VirtualBox
.exefile. -
If Windows shows a security prompt, click Yes.
The VirtualBox Setup Wizard will open.
Step 5: Choose Installation Options
During installation, you’ll see several setup screens. Don’t worry — the default options work perfectly for most users.
Here’s what you’ll see and what to do:
Welcome Screen
Click Next.
Custom Setup Screen
You’ll see options like:
-
VirtualBox Application
-
USB Support
-
Networking
-
Python Support
Leave everything checked and click Next.
These components allow VirtualBox to communicate with your network, USB devices, and system hardware.
Step 6: Network Interface Warning (Important to Know)
At one point, Windows will display a warning saying that network connections may be reset temporarily.
This happens because VirtualBox installs virtual network adapters.
Don’t panic — this is normal.
-
Your internet may disconnect for a few seconds.
-
It will automatically reconnect after installation.
Click Yes to continue.
Step 7: Start Installation
Click Install.
Windows may ask for permission to install device software — allow it.
Installation usually takes 2–3 minutes. During this time:
-
Network drivers are installed
-
VirtualBox system files are added
-
Virtual adapters are configured
Once finished, you’ll see a completion screen.
Check “Start Oracle VM VirtualBox after installation” and click Finish.
Step 8: Install the VirtualBox Extension Pack
This step is optional but highly recommended.
To install the Extension Pack:
-
Double-click the downloaded Extension Pack file
OR -
Open VirtualBox → File → Tools → Extensions
-
Click the + (Add) icon
-
Select the Extension Pack file
-
Accept the license agreement
-
Click Install
You may be asked for administrator permission — approve it.
Once installed, the Extension Pack will appear in the Extensions list.
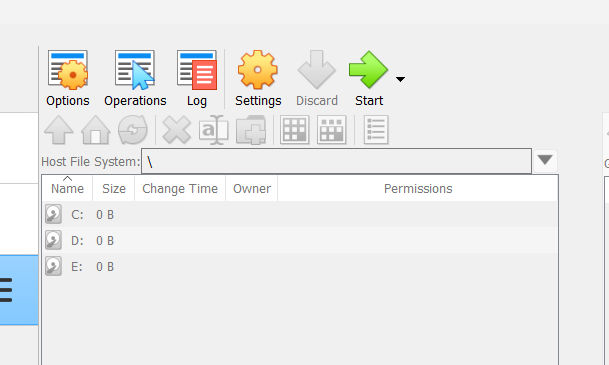
Step 9: Verify VirtualBox Installation
After installation, VirtualBox should open automatically.
You’ll see:
-
A clean interface
-
A left panel for virtual machines (currently empty)
-
A toolbar with options like New, Settings, Start
If VirtualBox opens without errors, installation is complete.
At this point, you’re ready to:
-
Create a virtual machine
-
Install Linux, Windows, or another OS
-
Experiment safely without touching your main system
Common Installation Issues and How to Fix Them
From experience, here are a few common hiccups and simple fixes:
VirtualBox won’t open or crashes
-
Make sure virtualization is enabled in BIOS
-
Disable Hyper-V, Windows Sandbox, and Virtual Machine Platform
-
Restart after making changes
64-bit systems not showing
-
Virtualization is disabled
-
Hyper-V is conflicting
Network not working inside VM
-
Recheck network adapter settings
-
Restart host machine
Most issues are one-time setup problems and don’t return once fixed.
Final Thoughts
Installing VirtualBox on Windows 11 is much easier than it sounds. Once it’s set up, it becomes one of the most useful tools you can have — especially if you like learning, testing, or working in multiple environments.
What I personally love about VirtualBox is the freedom it gives. You can experiment without fear, learn new skills safely, and explore operating systems without committing your entire computer to them.
In the next step, you can move on to creating your first virtual machine — and that’s where the real fun begins.
Disclaimer (Bazaronweb.com)
The information provided in this article is for educational and general guidance purposes only. Installation steps, system behavior, and results may vary depending on hardware configuration, BIOS/UEFI settings, Windows 11 version, and security policies. Bazaronweb.com is not responsible for system instability, data loss, virtualization conflicts, or software issues that may occur while installing or using VirtualBox.
VirtualBox, Oracle, Windows, and all related product names and trademarks belong to their respective owners. Bazaronweb.com is not affiliated with Oracle Corporation.
Written by Bazaronweb
Latest Tech Articles
- Microsoft Edge Not Responding on Windows 11? 9 Proven Fixes That Actually Work in 2026

- How to Create a Device Manager Shortcut on Windows (Fastest Desktop Access Guide for 2026)
- How to Record Videos With Background Music on iPhone (iOS 18 Guide)

- How to Unhide Apps on iPhone in 2026: Step-by-Step Guide

- Fix iPhone App Icons Turn Grey or Show “Waiting” After iOS Update

Products
-
![Apple Watch Ultra 3 [GPS + Cellular 49mm] Running & Multisport Smartwatch w/Rugged Titanium Case w/Black Titanium Milanese Loop - M. Satellite Communications, Advanced Health & Fitness Tracking](https://bazaronweb.com/retailstores/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/apple-watch-320x320.jpg) Apple Watch Ultra 3 [GPS + Cellular 49mm] Running & Multisport Smartwatch w/Rugged Titanium Case w/Black Titanium Milanese Loop - M. Satellite Communications, Advanced Health & Fitness Tracking
Apple Watch Ultra 3 [GPS + Cellular 49mm] Running & Multisport Smartwatch w/Rugged Titanium Case w/Black Titanium Milanese Loop - M. Satellite Communications, Advanced Health & Fitness Tracking
-
 Apple iPad mini (A17 Pro): Apple Intelligence, 8.3-inch Liquid Retina Display, 256GB, Wi-Fi 6E, 12MP Front/12MP Back Camera, Touch ID, All-Day Battery Life — Purple
Apple iPad mini (A17 Pro): Apple Intelligence, 8.3-inch Liquid Retina Display, 256GB, Wi-Fi 6E, 12MP Front/12MP Back Camera, Touch ID, All-Day Battery Life — Purple
-
 Apple AirPods Max Wireless Over-Ear Headphones, Active Noise Cancelling, Transparency Mode, Personalized Spatial Audio, Dolby Atmos, Bluetooth Headphones for iPhone – Space Gray
Apple AirPods Max Wireless Over-Ear Headphones, Active Noise Cancelling, Transparency Mode, Personalized Spatial Audio, Dolby Atmos, Bluetooth Headphones for iPhone – Space Gray
-
 Apple AirPods Pro 2 Wireless Earbuds, Active Noise Cancellation, Hearing Aid Feature, Bluetooth Headphones, Transparency, Personalized Spatial Audio, High-Fidelity Sound, H2 Chip, USB-C Charging
Apple AirPods Pro 2 Wireless Earbuds, Active Noise Cancellation, Hearing Aid Feature, Bluetooth Headphones, Transparency, Personalized Spatial Audio, High-Fidelity Sound, H2 Chip, USB-C Charging
-
 Leo Creation 144 TC Cotton Double Jaipuri Prints Flat Bedsheet(Pack of 1, Blue, Gree, Red, Grey, Light Grey)
Leo Creation 144 TC Cotton Double Jaipuri Prints Flat Bedsheet(Pack of 1, Blue, Gree, Red, Grey, Light Grey)
₹2,999.00Original price was: ₹2,999.00.₹329.00Current price is: ₹329.00.
Leave a Reply